Copper is known to possess certain unique qualities that make it the best engineering material for bearing applications. An ion is surrounded by a typical number of opposite charges.

Good Day Sunshine Vortex Orgone Pyramid 3 5 Inch Base Etsy Sacred Geometric Pure Copper Blue Calcite
Graphite is a covalent-network type of crystalline solid.

. View Homework Help - Apex Learning - Practice Assignment Energy in Matterpdf from CHEMISTRY 2 103-08 at Apex Alternative Ed. Metallic copper Network Covalent diamond Noble gases. 31 Which of the following is an example of ionic solid.
An amorphous solid forms small cryalline grains that assemble to make a larger structure. For example in NaCl the Na ion is surrounded by 6 Cl- ions. Since carbon atoms have properties for catenation they form covalent bonds with each other in a 3 D frame network.
1 ionic 2 metallic 3 covalent network and 4 molecular. Amorphous Solids They do not have sharp melting points. Hard and brittle.
These solids are formed in a process known as crystallization wherein the lattice structure. You may view the structure of copper. Name the type of crystalline solid formed from the following structural units and describe solid is formed.
A possible crystal structure of Copper is face-centered cubic structure. 32 What is holding atoms together. Lattice points made of atoms.
Crystalline substances can be described by the types of particles in them and the types of chemical bonding that takes place between the particles. Diamond consists of a three dimensional network of carbon atoms attached to each other. Interactively best but the page will take longer to load or.
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu from Latin. Three types of Atomic solids. Metal atoms 1.
Conduct electricity and heat when molten The unit cell has the same composition ratio of cations to anions as the empirical formula. Metallurgy of Copper-Base Alloys. Western Reserve Manufacturing Co Inc.
Crystalline solids include metallic ionic network atomic and molecular solids and true solids. 29 What are the 5 types of solids. Answer 1 of 2.
Crystalline solids are those in which the atoms ions or molecules that make up the solid exist in a regular well-defined arrangement. There are four types of crystals. Most solid metals have crystalline structures.
The change in enthalpy when a substance is heated to change its state from solid to liquid Crystalline Solids They have definite heat of fusion. Ionic solids Made up of positive and negative ions and. Copper crystal structure image space filling style.
Properties and several examples of each type are listed in the. Ionic solids consist of and ions Ions are held together by very strong ion-ion electrostatic attractions ionic bonds Examples. In metals and in many other solids the atoms are arranged in regular arrays called crystals.
Unlike amorphous solids that melt at a range of temperatures crystalline solids have definite melting points. Copper crystal structure image ball and stick style. Copper Crystal Structure.
Copper has a face-centered cubic structure. By definition a crystalline solid also simply known as a crystal is a solid material whose basic constituents such as atoms ions and molecules are arranged in a highly ordered and well-defined microscopic structure known as a crystal lattice. Force and properties of network covalent solid.
Force and property of Mettalic solid. The basic properties of copper alloys are largely influenced by the properties of copper itself. A crystal lattice is a repeating pattern of mathematical points that extends throughout space.
It is a soft malleable and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivityA freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange colorCopper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity as a building material and as a constituent of various metal alloys such as. Covalent bond Hard and high melting point. An amorphous solid forms when larger and smaller molecules combine in an orderly fashion.
The solid tends to soften gradually over a temperature range. Crystalline solids consist of atoms ions and molecules arranged in definite and repeating three-dimensional patterns. An amorphous solid forms when a substance freezes very quickly and doesnt have time to form an orderly lattice.
Cuprum and atomic number 29. A crystalline solid is a solid that is made up of crystals in which particles are arranged in a regular repeating pattern. 33 Which electrostatic forces hold atoms together in a.
The intermolecular covalent bonds make it hard. There are two main categories of solids. 2222021 Apex Learning - Practice Assignment 151 Practice.
The forces of chemical bonding causes this repetition. Classes of Crystalline Solids. 30 How are covalent network solids similar to ionic solids.
28 What kind of crystalline solid is copper apex. Hence diamond is an example of network covalent solid. Ions in these solids are held together by strong electrostatic forces.
Metallic Bond Excellent conductor. Crystalline Solids They have a sharp melting point. Amorphous means having a non-crystalline structure.
2 points how the i. Metallic crystals arent perfect but loaded with defects. Constituent particles in ionic solids of the Crystalline Solids are anions negatively charged and cations positively charged.
Copper Mineral Information Data And Localities

Copper Mineral Information Data And Localities
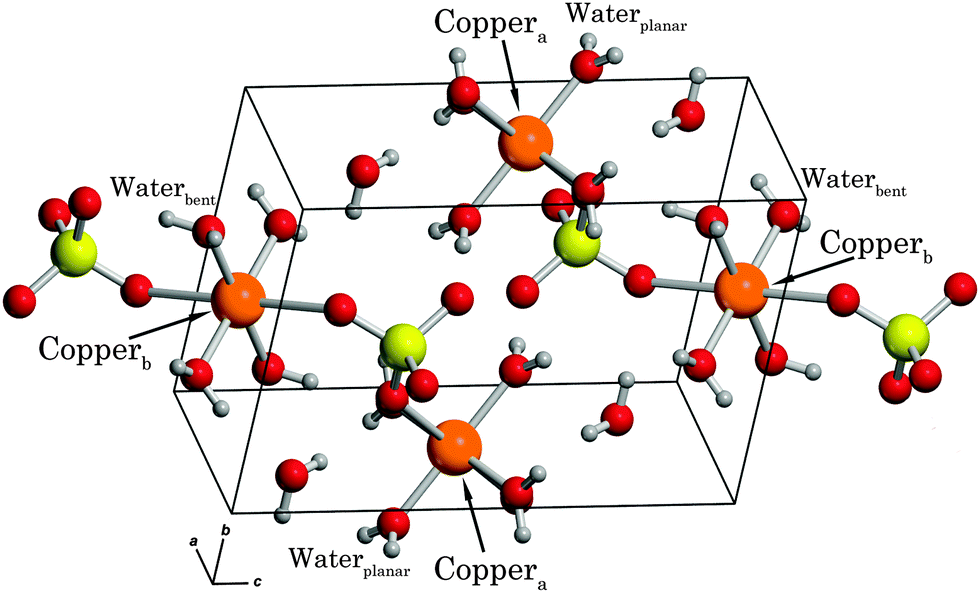
Origins Of Contrasting Copper Coordination Geometries In Crystalline Copper Sulfate Pentahydrate Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics Rsc Publishing Doi 10 1039 C5cp05554g

0 Comments